Holistic thinking meets white board planning
A new way to share information born from holistic thinking

A Revolutionary Approach to Farm Management with Whiteboards
You might be thinking, "Well, this isn’t very interesting or groundbreaking," but let me share why this simple system could be a game-changer for certain farms. It’s born from a deep understanding of Holistic Management (HM) and has the potential to transform how farms operate.
When we visited Francisco Alves at his farm, Herdade de São Luís in Portugal, last September, he couldn’t wait to show us his farm office and the ingenious management system he’s developed. It’s a system inspired by HM principles that he’s applied to every aspect of his farm operations.
A Simple Yet Effective Farm Office
Francisco’s farm office is modest and refreshingly simple. There are no computers, no filing cabinets—just large whiteboards covering the walls and plenty of marker pens. It’s the kind of setup that immediately feels approachable. This simplicity embodies a key HM principle: involving everyone in the decision-making process.
These whiteboards make the farm’s operations transparent and accessible. Whether it’s Antonio, the farm manager, or one of the interns, anyone can walk into the room, glance at the boards, and find the information they need—no logging into computers or sifting through paperwork required.
Organised and Comprehensive Information
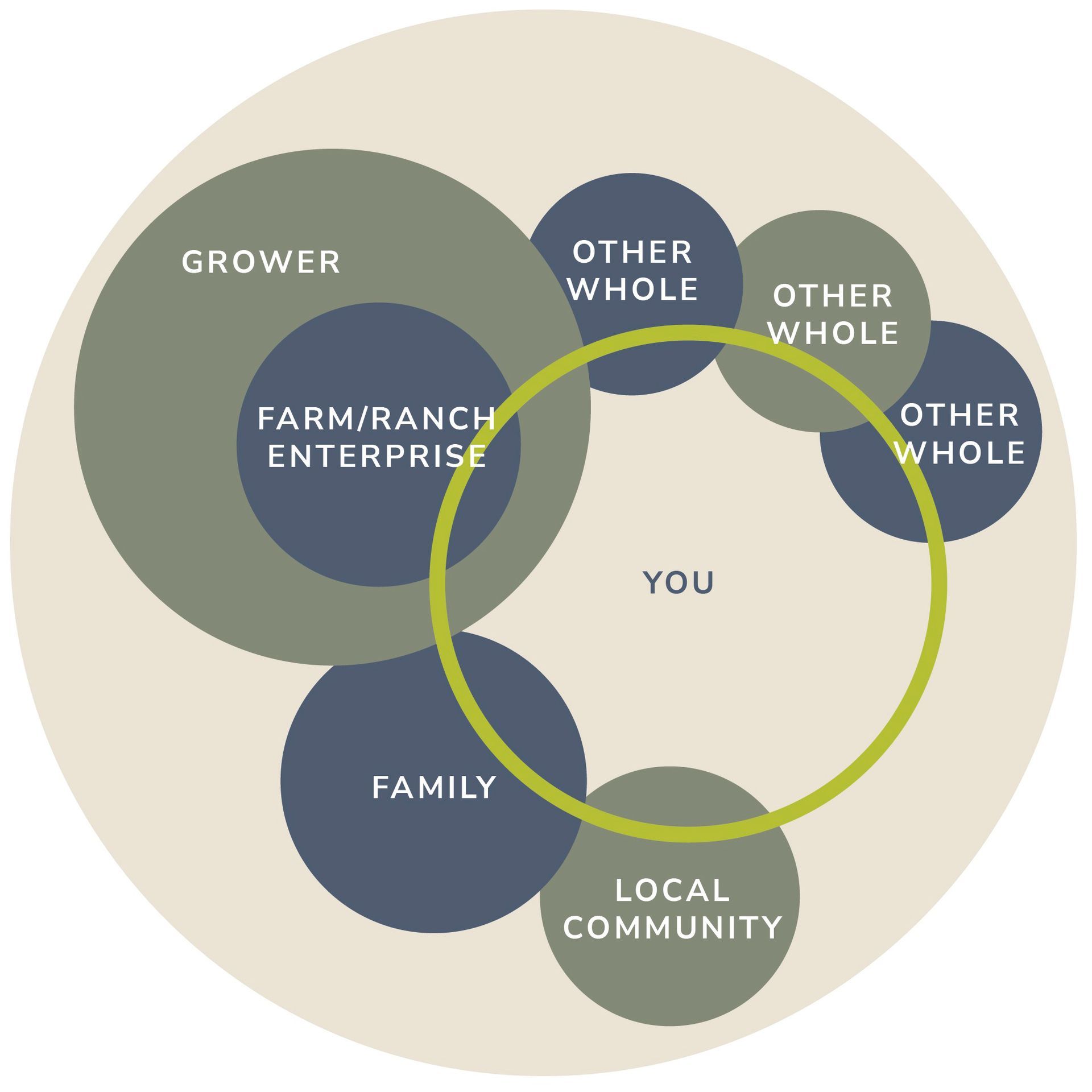
The whiteboards are divided into sections, each focusing on different aspects of farm management—grazing plans, crop rotations, financial budgets, and more. They display key information such as weather patterns, pest control measures, and livestock statistics in a clear and visually engaging way.
One of the most innovative features of this system is how it treats cows, sheep, goats, and pigs as individual “companies.” Each species has its own section, with management plans, inputs, and outputs tracked meticulously. This allows Francisco to assess the profitability and ecological impact of each species while also highlighting how they contribute to the farm’s ecosystem as a whole. Processes like the water cycle, nutrient flow, and energy flow are also mapped out, showing how each species plays a part in maintaining the farm’s balance.
Enhancing Collaboration and Decision-Making
This system is more than just organised—it’s collaborative. From Antonio to the farm’s interns, everyone can contribute to or update the boards. This shared ownership ensures the system remains dynamic and responsive. It also makes it easy to spot trends, such as livestock births or pasture usage, and adjust plans as needed.
Colour-coded markers and tags make prioritisation and categorisation intuitive. The iterative and adaptive nature of this approach is a perfect fit for HM principles, encouraging transparency and proactive decision-making while reducing inefficiencies.
Addressing Potential Challenges
I had to ask Francisco about the obvious risk: what happens if someone accidentally wipes off part of the board? He grinned and said, "It’s no problem. Every two days, I take a picture on my phone. At the end of the season, we transfer everything we need into the computer." It’s a simple yet effective way to ensure no data is lost, maintaining the system’s practicality without overcomplicating it.
A System Born from Holistic Thinking
When we first stepped into the office, Francisco joked that he wasn’t a very organised person. Honestly, after seeing this system, I have to disagree. The whiteboard setup is incredibly organised, beautifully simple, and a true reflection of holistic thinking. By blending ecological, economic, and social dimensions into a single cohesive strategy, Francisco has created a management system that’s as effective as it is sustainable.
In the end, this whiteboard-based approach is a testament to how simplicity, combined with a deep understanding of HM principles, can revolutionise farm management. It makes day-to-day operations easier while setting a strong foundation for long-term sustainability. It’s a system that’s not just practical—it’s inspiring.
Film below gives more details on this system